Precision pendulum clocks – Masterpieces of timekeeping
19. Jun 2024
Immerse yourself in the world of precision pendulum clocks and regulator pulley clocks, two icons of timekeeping. In this article, we explore the subtle but crucial differences between these two types of clocks. Learn more about the technical features of precision pendulum clocks and be inspired by the precision and sophistication of these timepieces. Discover how precision pendulum clocks with compensation pendulum and barometer instrument differ from other regulators and what makes these clocks so exceptional.
The pendulum
The pendulum is still today’s most accurate mechanical oscillation device. The accuracy of a clock pendulum is determined by constant length, constant small amplitude and a constant force of gravity. This time-keeping breakthrough was discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1585. According to his observations, a pendulum has always the same oscillation time (period) regardless of its amplitude. This principle is called ‘isochronism’. Strictly speaking it only holds at very small amplitudes. In conclusion one can say that the accuracy of a clock pendulum is determined by constant length, constant small amplitude and a constant force of gravity.
But the length of a pendulum is dependent on external influences like temperature. An increase in temperature results in the expansion of almost all solid materials. When it cools down, the pendulum rod contracts and becomes shorter. The result is a longer period at higher temperatures and a shorter period at lower temperatures. The small, temperature-related changes in length of our Invar pendulum rods are also compensated for by a precisely calculated, freely movable compensation tube. This means that there is no change in length when the temperature increases or decreases. The effective pendulum length remains the same and so does the rate of the clock.
Air pressure compensation by using the barometer instrument
In addition to temperature changes, the effect of which is compensated for by the temperature compensation, air pressure fluctuations also cause gear changes. As a result, in the event of extreme pressure changes of 100 mbar, a pendulum clock’s accuracy can change by approximately one to two seconds per day, as shown by measurements on our own pendulum test stand. To counterbalance these deviations, Riefler developed the concept of air pressure compensation using aneroid capsules, as can already be seen in aneroid barometers and barometric altimeters.
A good precision pendulum clock is characterised by steady motion and is not affected by outside interferences. The barometer instrument compensates for accuracy fluctuations that are caused by air-pressure changes. To be more precise, we are referring to changes in air density or air weight that are proportionally related to the air pressure. Accuracy fluctuations caused by increasing air density result from the pendulum’s increased lift. Together with other influence factors, such as increased air resistance, this causes the pendulum swing to slow down. The compensation function depends on changes to the pendulum’s moment of inertia caused by moving a mass on the pendulum rod, and causes the period of oscillation to change. When using this kind of compensation, movement is caused by the five aneroid capsules or barometer capsules with the weight on them. Each of these capsules consists of two thin metal membranes that are soldered together in a vacuum. If the air pressure outside these capsules increases, they are pushed together and the counterweight lowers. Thanks to the capsule design, temperature influences do not affect the total stroke.
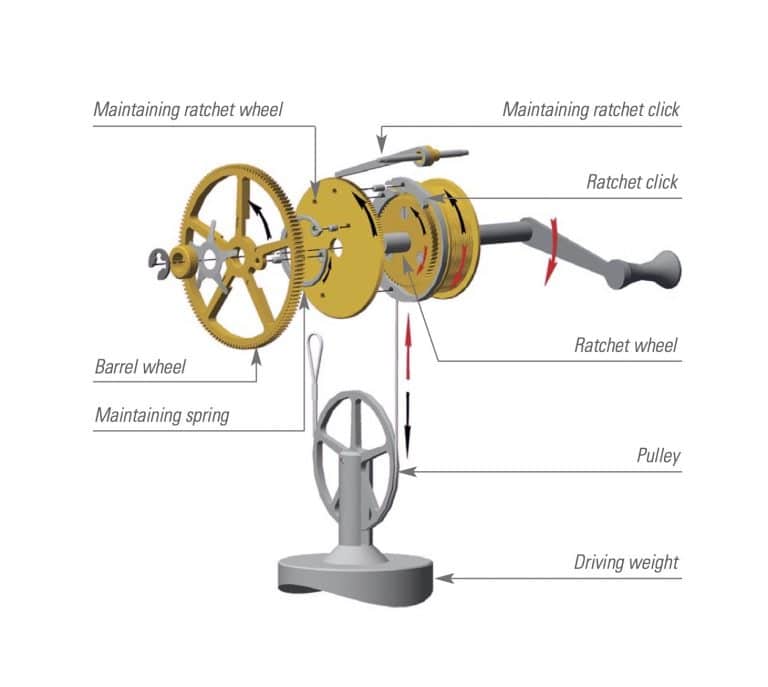
The maintaining power mechanism
While you are winding a precision pendulum clock, the steel cable is coiled onto the barrel, moving the weight upwards. Because the weight cannot act on the gear train during this time, the clock would not be driven during the winding process, so the time display would remain behind. This is prevented in every Sattler precision pendulum clock by a so-called maintaining power mechanism on the barrel arbor.
The accuracy of a precision pendulum clock in comparison
In summary, a precision pendulum clock is characterized by a very high rate accuracy of (at best) 1 to 2 seconds per month, while a regulator pulley clock achieves an accuracy of around 10 seconds per week. The pendulum rods of the precision pendulum clock are made of Invar, a special alloy that enables precise temperature compensation. In addition, the pendulum of the precision pendulum clock is tested in a measuring and testing laboratory.
The running time of a precision pendulum clock is usually one month, whereas the running time of a regulator pulley clock is between one week and one month. A precision pendulum clock is also characterized by a maintaining power and jewel pallets as well as a counterweight on the minute hand. The fine adjustment of the precision pendulum clock is carried out using a special fine adjustment table.



Post from

Julia Rick
Julia Rick was born and raised in Munich. After graduating from the European School in Munich, she trained as a commercial specialist in the field of jewelry and watches. She is currently studying for a Master's degree in International Management and works at Erwin Sattler in the areas of HR management and online marketing.
Discover more Posts








